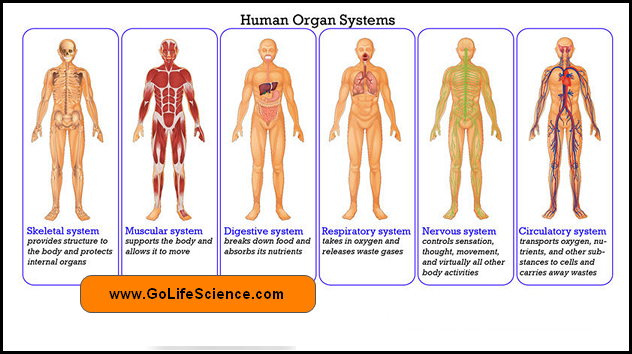
A human body system is a complex machine, made up of different systems. The various human body systems by their coordinate activities function in unison and work efficiently carrying out the vital body functions.
Important human body systems
1. Digestive system:
The digestive system helps in food digestion. The organs involved in this process are:
- Alimentary canal
- Mouth
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- Gullet
- Stomach
- Large intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
- Glands
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Secretions or Enzymes
- Gastric Juice
- Pancreatic juice
- Bile Juice
2. Circulatory system:
William Harvey (1578-1657) was the discoverer of the process of blood circulation. The central organ of the blood circulatory system is the Heart. On average, the heart beats about 2600 million times in a man’s life and pumps 155 million liters i.e., 150,000 tonnes of blood from each ventricle.
The system helps in transportation inside the body. It consists of the following components:
- Blood
- Plasma
- Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
- Red Blood Cells
- Blood Platelets
- Blood Groups
- A-group
- B-Group
- AB-Group
- O-Group
- Heart
- Veins
- Arteries

3. Nervous system:
the Nervous system is important rather essential for the regulation, control, and coordination of body functions. It enables the individual function,
- To respond in a coordinated manner to environmental changes
- To co-ordinate and control various movements, which may be muscular, secretomotor or otherwise
- To prolong life by protecting the body against harmful stimuli
The system helps in sensory functions and consists of:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Veinous nerves
- Spinal nerves
- Sensory nerves
- Motor nerves
4. Respiratory system:
Respiration is the process of gaseous exchange between an organism and its environment. This helps in the gaseous exchange and intake of oxygen. The organs are:
- Nostrils
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles (segmental and terminal)
- Respiratory bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
- Lungs
5. Endocrine Systems:
It consists of ductless glands which secrete their juice directly into the blood. They are:
Read more: Endocrine system and Homeostasis in Vertebrates
6. Excretory system:
It helps in the removal of wastes from the body. It includes-
- Kidney
- Nephron
- Urethra
- Urinary Bladder
Digestive Enzymes and their Functions
- Amylase – starch digestion
- Trypsin – Protein digestion
- Pepsin – Protein digestion
- Maltase – Maltose (Disaccharide) digestion
- Sucrase – Sucrose (Disaccharide) digestion

